Inner binding energyThe energy required to separate particles which are bound by... of atomic nuclei. The nuclear building blocks show various degrees of mutual binding from one atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d... type to another. The maximum binding energyThe energy required to separate particles which are bound by... per nuclear building block is within the range of the mass numberMass of an atom in nuclear mass units. Number of protons and... 60. By means of nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... conversionIn nuclear technology the conversion of a substance in a fis..., energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... can therefore be obtained either by fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. of heavy nuclei such as uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... or by fusionFormation of a heavy nucleus from lighter nuclei releasing e... of lighter nuclei such as hydrogen. The fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. of 1 kg U-235 supplies about 23 million kWh, during the fusionFormation of a heavy nucleus from lighter nuclei releasing e... of deuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... and tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... (DT-reaction) to 1 kg helium, energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of about 120 million kWh is released. In contrast, the combustion of 1 kg coal supplies only about 10 kWh. (See ‘fusion’ and ‘nuclear fission’.)
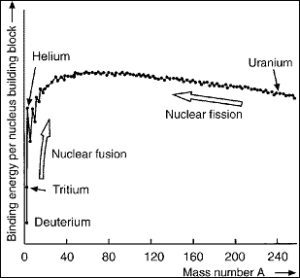
Nuclear binding energyThe energy required to separate particles which are bound by... depending on the mass numberMass of an atom in nuclear mass units. Number of protons and... of the nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... of the atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d...
