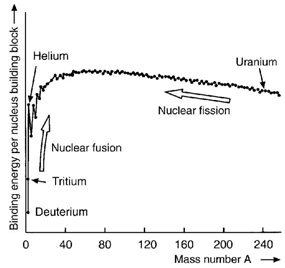
The energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... required to separate particles which are bound by electromagnetic or nuclear forces (infinitely far apart). In the case of the nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... of an atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d..., these particles are protons and neutrons held together by the nuclear binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th.... The neutronUncharged elementary particle with a mass of 1.67492716 ·10... and protonElementary particle with a positive electrical elementary ch... binding energies are the energies necessary to release a neutronUncharged elementary particle with a mass of 1.67492716 ·10... or protonElementary particle with a positive electrical elementary ch... from the nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts .... ElectronElementary particle with a negative electrical elementary ch... binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... is the energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... required to completely remove an electronElementary particle with a negative electrical elementary ch... from an atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d... or a moleculeAn atomic group held together by chemical forces. The atoms .... The binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of nucleons in the nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... of an atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d... amounts for most nuclei (i.e. Z>5) to around 8 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV. per nucleonGroup name for protons and neutrons.. However in the case of the heaviest nuclei of an atomSmallest particle of an element which cannot be chemically d..., such as uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n..., the binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... per nucleonGroup name for protons and neutrons. is slightly less negative than for nuclei with medium mass numbers. Therefore, the fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. of an uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... into two nuclei of medium mass numberMass of an atom in nuclear mass units. Number of protons and... results in a total more negative binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... leading to energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... being released to the outside (See also ‘nuclear fission’). Similarly the binding energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of the light nuclei of the hydrogen isotopes deuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... and tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... is significantly less negative than that of the helium nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... He-4. Thus, energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... is released during the fusionFormation of a heavy nucleus from lighter nuclei releasing e... of deuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... and tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... to helium (See also ‘fusion’).
Diagram binding energy