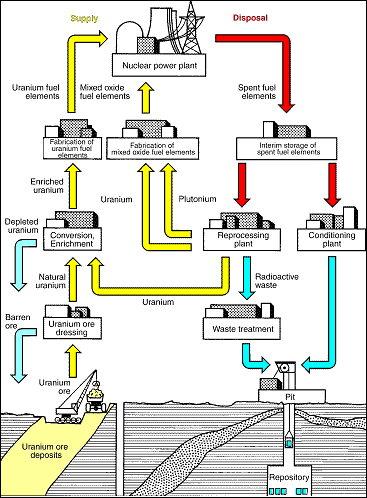
A number of process stages in the supply and waste managementAll facilities and process steps in nuclear engineering requ... of nuclear fuelIn accordance with the definition of the German Atomic Energ... for reactors.
- Supply:
The point of departure of nuclear energyInner binding energy of atomic nuclei. The nuclear building ... utilization is the supply of nuclear reactors with uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n.... The uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... content of mined ores amounts typically to 0.2%. The uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... is concentrated in a treatment process. The commercial article “Yellow Cake” results, which contains about 70 to 75% uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n.... The uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... contained in the Yellow CakeYellow cake is the final product of the milling of uranium o... has a natural isotopeAtoms of the same atomic number (i.e. the same chemical elem... composition of 0.7% U-235 and 99.3% U-238. Most nuclear power plants need uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... with a proportion of 3 to 5% of the fissile isotopeAtoms of the same atomic number (i.e. the same chemical elem... U-235. Therefore, the uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... must be enriched to U-235. For this purpose the uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... is converted into the chemical compound UF6, which can easily be transferred to the gas phase, since enrichmentProcess by which the share of a certain isotpe in an element... is only easily possible in the gas phase. EnrichmentProcess by which the share of a certain isotpe in an element... processes (See ‘gas centrifuge’ or ‘diffusion separation processes’) use the slight mass difference of the U-235 and U-238 molecules of UF6 to separate these two components. The product of the enrichmentProcess by which the share of a certain isotpe in an element... plant is UF6 with a U-235 share of approx. 3 to 5%. In the fuel elementArrangement of a number of fuel rods into which the nuclear ... factory, the UF6 is converted into UO2. The UO2 powder is used to press pellets which are sintered at temperatures of more than 1700 °C, filled into seamlessly drawn claddingTightly bound (usually metallic) casing directly surrounding... tubes made of a zirconium alloy and sealed gas-tight. Thus, individual fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. rods are obtained which are then grouped into fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements. The fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements of a pressurized water reactorPower reactor in which the heat is dissipated from the core ... contain about 340 kg uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n..., those of a boiling water reactorNuclear reactor with water as a coolant and as a moderator, ... about 190 kg uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n.... - Waste managementAll facilities and process steps in nuclear engineering requ...:
The service periodreactor period of fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements in the reactorSystem used to initiate, maintain and control a fission chai... is three to four years. Nuclear energyInner binding energy of atomic nuclei. The nuclear building ... is converted to electricity by nuclear fissionFission of an atomic nucleus into two parts of the same size.... During this process the percentage of fissile U-235 decreases, and the partly radioactive fission productsNuclides generated by fission or subsequent radioactive deca... and considerable quantities of the new, partly fissile nuclear fuelIn accordance with the definition of the German Atomic Energ... plutoniumPlutonium - the 94th element in the classification of elemen... are generated. All activities relating to treatment, reprocessingApplication of chemical processes to separate the valuable s... and disposal of fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements are summarized under the term waste managementAll facilities and process steps in nuclear engineering requ.... Two types of disposal are possible: reprocessingApplication of chemical processes to separate the valuable s... by recovery and reuse of the usable plutoniumPlutonium - the 94th element in the classification of elemen... and uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... portions or direct ultimate waste disposal where the spent fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements are disposed of altogether as waste. The fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements are stored initially in an interim storage facility where the activityActivity is the term used to characterise the number of nucl... decreases. During subsequent reprocessingApplication of chemical processes to separate the valuable s..., reusable uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... and plutoniumPlutonium - the 94th element in the classification of elemen... are separated from the radioactive fission productsNuclides generated by fission or subsequent radioactive deca.... For reuse in the nuclear power plantThermal power plant, primarily used for electricity generati... plutoniumPlutonium - the 94th element in the classification of elemen... and uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... – possibly after enrichmentProcess by which the share of a certain isotpe in an element... – must be processed into fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements. With their use in the nuclear power plantThermal power plant, primarily used for electricity generati... the fuel cycleSee 'nuclear fuel cycle'. closes. In the case of the direct ultimate waste disposal, the entire fuel elementArrangement of a number of fuel rods into which the nuclear ... including the valuable substances uraniumNatural radioactive element with the atomic number 92. The n... and plutoniumPlutonium - the 94th element in the classification of elemen... is disposed of as radioactive waste following an interim storage periodreactor period to allow the short-lived radionuclidesThe Radiological Protection Ordinance defines radioactive su... to decayThe spontaneous conversion of a nuclide into another nuclide... and thus the heat development conditional on the decayThe spontaneous conversion of a nuclide into another nuclide... to decline. For this purpose the fuelSee 'nuclear fuel'. elements are sectioned in a conditioning plant, packed in containers suitable for final storage before being stored in a repository. Both methods – reprocessingApplication of chemical processes to separate the valuable s... and direct ultimate storage – have been thoroughly examined in Germany and the required processes and components have been developed. Radioactive waste must be stored safely for a long periodreactor period and be kept away from biosphereSphere of life for all organisms on earth; it reaches only a.... Under certain circumstances low and medium active liquid radioactive waste is fixed in cement following previous volume reduction by evaporation. Solid radioactive waste is burnt or compacted for volume reduction. For ultimate storage these products are packed in special barrels or containers. The highly active, heat-generating fissionSee 'nuclear fission'. product solutions from reprocessingApplication of chemical processes to separate the valuable s... are vitrified in a well-tested procedure adding glass-forming substances and filled into stainless steel containers. Stable geological formations are used as repositories. In Switzerland and in Sweden granite rock is provided for this purpose and in Germany salt domes were investigated for ultimate waste disposal. Rock salt offers excellent properties for the ultimate disposal of heat-generating radioactive waste since it removes the heat well and has plastic behaviour, i.e. cavities gradually close and the waste is safely embedded.
Nuclear fuelIn accordance with the definition of the German Atomic Energ...fuel cycleSee 'nuclear fuel cycle'.
