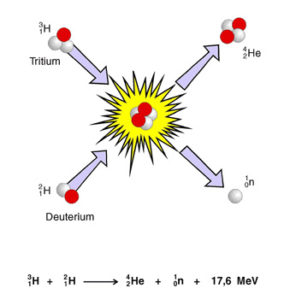
Formation of a heavy nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... from lighter nuclei releasing energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... – the binding energyThe energy required to separate particles which are bound by.... Possible fusion reactions:
D + T -> 4He + n + 17.58 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.,
D + D -> 3He + n + 3.27 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.,
D + D -> T + p + 4.03 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.,
D + 3He -> 4He + p + 18.35 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.,
p + 11B -> 3 4He + 8.7 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV..
The deuterium-tritium reaction is the easiest to realize among all possible fusion reactions. DeuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... is available in sufficient quantity in the oceans of the world; tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... can be “bred” from the lithium elementChemical base material which cannot be chemically converted ... – which is also available in abundance – by means of the neutrons generated during the fusion process.
BreedingConversion of non-fissionable into fissionable material, e.g... reactors for the generation of tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... from lithium:
7Li + n -> 4He + T + n -2.47 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV.,
6Li + n -> 4He + T + 4.78 MeVMegaelectron volt, 1,000,000 eV..
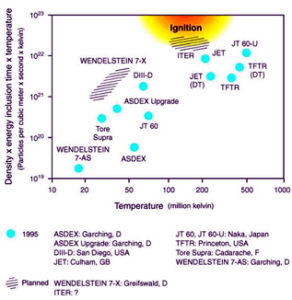
During fusion, two atomic nuclei – e.g. nuclei of the hydrogen isotopes deuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... and tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... – must be brought so close together that they fuse in spite of the repellent electric power of their positive nucleusPositively charged nucleus of an atom. Its diameter amounts ... charges. Two nuclei must fly against each other with high speed to overcome their mutual repulsion. The required speeds of the particles are achieved at high temperatures of about 100 million degrees. The atoms of a gas subsequently disintegrate into electrons and nuclei and the gas is ionized. A completely ionized gas is called plasmaElectrically neutral gas mixture of ions, electrons and neut.... PlasmaElectrically neutral gas mixture of ions, electrons and neut... is electrically conductive and its motion can therefore be influenced by electric and magnetic fields. Advantage is taken of this fact in fusion facilities where the hotA term used in nuclear technology for "highly active". plasmaElectrically neutral gas mixture of ions, electrons and neut... is enclosed by a magnetic field cage. In a magnetic field, the Lorentz force acts on the charge carriers. As a result of this force, the charge carriers perform a spiral movement along the magnetic field lines. Ideally, a contact with the container wall and thus heat transport to the wall needs to be prevented. As arrangements to magnetically enclose the plasmas within a ring the systems of the type TokamakExperimental arrangement for controlled nuclear fusion. In a... and stellaratorExperimental arrangement for controlled nuclear fusion. In a... (see ‘Tokamak’ and ‘stellarator’) are usual. (See also ‘JET’ and ‘ITER’). The main research targetPiece of matter on which radiation impinges, causing nuclear... in plasmaElectrically neutral gas mixture of ions, electrons and neut... physics is to find a suitable procedure allowing a controlled fusion reaction in the form of a chain reactionSelf-perpetuating reaction. In a fission chain reaction, a f... that enables use of the released energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th.... During the fusion of deuteriumHydrogen isotope with a nucleus containing a neutron and a p... and tritiumRadioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and a prot... to form 1 kg helium, an energyAbility to do work or diffuse heat. The unit of energy is th... of about 120 million kWh is released corresponding to a gross calorific value of 12 million kilograms of coal.